Updated:2025-03-13
Views:2357
 WeChat
WeChat
 QQ
QQ
 Online Service
Online Service
 User's Manual
User's Manual
Solar radiation at Earth’s surface is typically defined as total radiation across a wavelength range of 280 to 4000 nm (shortwave radiation). Total solar radiation, direct beam and diffuse, incident on a horizontal surface is defined as global shortwave radiation, or shortwave irradiance (incident radiant flux), and is expressed in Watts per square meter (W m-2, equal to Joules per second per square meter).
Pyranometers are sensors that measure global shortwave radiation. Apogee SP series pyranometers are silicon-cell pyranometers and are only sensitive to a portion of the solar spectrum, approximately 350-1100 nm (approximately 80 % of total shortwave radiation is within this range). However, silicon-cell pyranometers are calibrated to estimate total shortwave radiation across the entire solar spectrum. Silicon-cell pyranometer specifications compare favorably to specifications for World Meteorological Organization (WMO) moderate and good quality classifications and specifications for International Organization of Standardization (ISO) Class C classification, but because of limited spectral sensitivity, they do not meet the spectral specification necessary for WMO certification.
Typical applications of silicon-cell pyranometers include incoming shortwave radiation measurement in agricultural, ecological, and hydrological weather networks, and solar panel arrays.
Apogee Instruments SP series pyranometers consist of a cast acrylic diffuser (filter), photodiode, and signal processing circuitry mounted in an anodized aluminum housing, and a cable to connect the sensor to a measurement device. Sensors are potted solid with no internal air space and are designed for continuous total shortwave radiation measurement on a planar surface in outdoor environments. SP series sensors output an analog voltage that is directly proportional to total shortwave radiation from the sun. The voltage signal from the sensor is directly proportional to radiation incident on a planar surface (does not have to be horizontal), where the radiation emanates from all angles of a hemisphere.
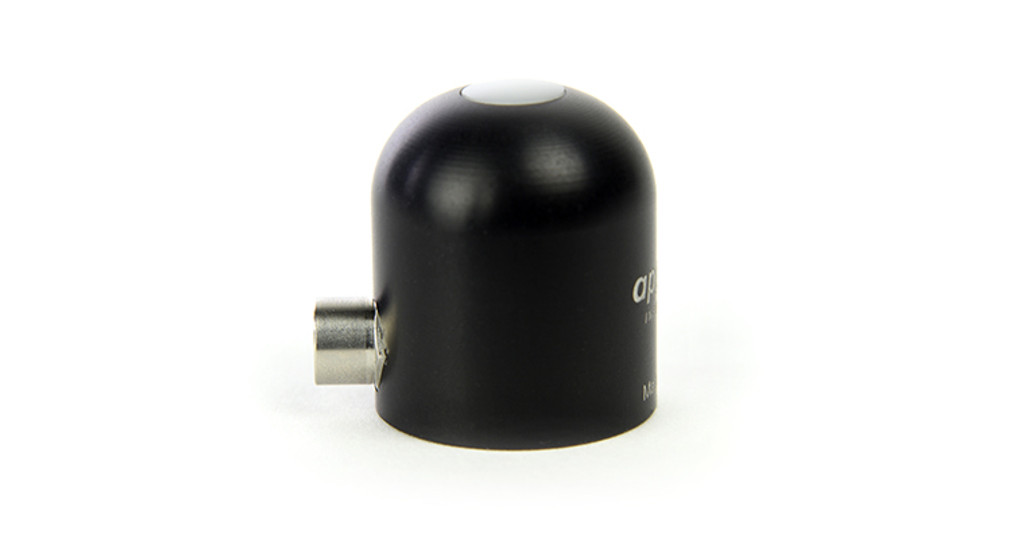
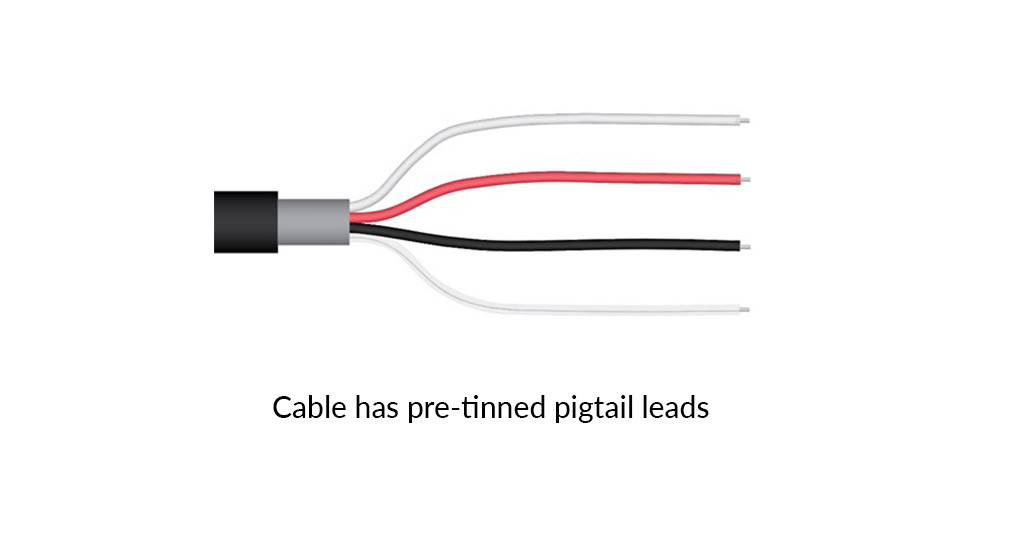
The SP-215 is an amplified, analog sensor with a 0 to 5.0 V output. The sensor incorporates a silicon-cell photodiode with a rugged, self-cleaning sensor housing design, and high-quality cable terminating in pre-tinned pigtail leads for easy connection to dataloggers and controllers. Typical applications include shortwave radiation measurement in agricultural, ecological, and hydrological weather networks. Sensors are also used to optimize photovoltaic systems. Sensor includes IP68 marine-grade stainless-steel cable connector to simplify sensor removal and replacement for maintenance and recalibration.

| ISO 9060:2018 | Class C (fast response) |
| Class C (fast response) | 5.5 to 24 V DC |
| Current Draw | 300 µA |
| Sensitivity | 2.5 mV per W mˉ² |
| Calibration Factor | 0.4 W mˉ² per mV (reciprocal of sensitivity) |
| Calibration Uncertainty at 1000 W mˉ² | Less than 3 % |
| Calibrated Output Range | 0 to 5 V |
| Measurement Repeatability | Less than 1 % |
| Non-stability (Long-term Drift) | Less than 2 % per year |
| Non-linearity | Less than 1 % (up to 2000 W mˉ², maximum radiation measurement is 2000 W mˉ²) |
| Response Time | Less than 1 ms |
| Field of View | 180˚ |
| Spectral Range | 360 to 1120 nm (wavelengths where response is 10 % of maximum) |
| Directional (Cosine) Response | ± 5 % at 75˚ zenith angle |
| Temperature Response | 0.04 ± 0.04 % per C |
| Operating Environment | -40 to 70 C; 0 to 100 % relative humidity; can be submerged in water up to depths of 30 m |
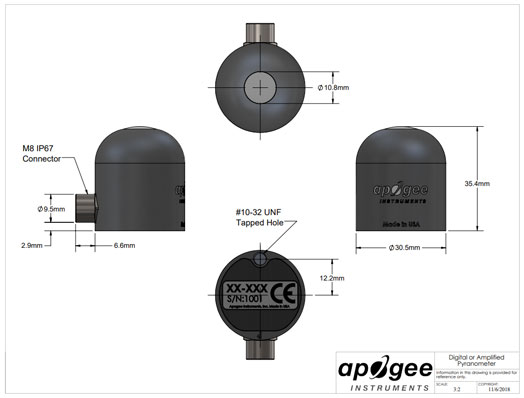
| Dimensions | 30.5 mm diameter, 37 mm height |
| Mass (with 5 m of cable) | 140 g |
| Warranty | 4 years against defects in materials and workmanship |
| Manufactured | Made in the USA |
Customer Service QQ
Customer Hotline:
Technical Supports